Corn
Corn is the most liquid grain market seeing increasing demand in the food and energy industries. This guide to trading corn unpacks live prices and opening hours, plus popular trading strategies and market economics. See our list of the top corn brokers in the UK to start trading:
Best Corn Trading Brokers
-
Founded in Australia in 2010, Pepperstone is a highly regarded broker specialising in forex and CFDs. Serving more than 400,000 clients globally, it provides access to over 1,300 financial instruments through popular platforms like MT4, MT5, cTrader, and TradingView. Its fee structure is both low and transparent. With regulation by reputable bodies such as the FCA, ASIC, and CySEC, Pepperstone guarantees a safe trading environment for traders at every level.
Instruments Regulator Platforms CFDs, Forex, Currency Indices, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, ETFs, Crypto (only Pro clients), Spread Betting FCA, ASIC, CySEC, DFSA, CMA, BaFin, SCB MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView, AutoChartist, DupliTrade, Quantower Min. Deposit Min. Trade Leverage $0 0.01 Lots 1:30 (Retail), 1:500 (Pro) -
Established in Poland in 2002, XTB caters to over a million clients worldwide. This forex and CFD broker offers a robust regulatory framework, a diverse range of assets, and prioritises trader satisfaction. It provides an intuitive proprietary platform equipped with excellent tools to support aspiring traders.
Instruments Regulator Platforms CFDs on shares, Indices, ETFs, Raw Materials, Forex currencies, cryptocurrencies, Real shares, Real ETFs FCA, CySEC, KNF, DFSA, FSC xStation Min. Deposit Min. Trade Leverage $0 0.01 Lots 1:30 -
IC Markets is an internationally acclaimed forex and CFD broker, admired for its competitive pricing, diverse trading instruments, and superior technology. Established in 2007 and based in Australia, the firm is under the regulation of ASIC, CySEC, and FSA. It has successfully drawn over 180,000 clients from more than 200 nations.
Instruments Regulator Platforms CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, Bonds, Futures, Crypto ASIC, CySEC, CMA, FSA MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView, TradingCentral, DupliTrade, Quantower Min. Deposit Min. Trade Leverage $200 0.01 Lots 1:30 (ASIC & CySEC), 1:500 (FSA), 1:1000 (Global) -
IC Trading belongs to the reputable IC Markets group. Designed for dedicated traders, it offers highly competitive spreads, dependable order execution, and sophisticated trading tools. However, it operates from Mauritius, an offshore financial centre, allowing high leverage but within a less regulated environment.
Instruments Regulator Platforms CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, Bonds, Cryptos, Futures FSC MT4, MT5, cTrader, AutoChartist, TradingCentral Min. Deposit Min. Trade Leverage $200 0.01 Lots 1:500 -
Fusion Markets, an online broker since 2017, operates under the regulation of ASIC, VFSC, and FSA. Renowned for offering cost-effective forex and CFD trading, it provides various account options and copy trading solutions to suit diverse trading needs. New clients can begin trading with a simple three-step registration process.
Instruments Regulator Platforms CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, Crypto ASIC, VFSC, FSA MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView, DupliTrade Min. Deposit Min. Trade Leverage $0 0.01 Lots 1:500 -
BlackBull, a New Zealand-based CFD broker, offers a wide range of trading options across more than 26,000 instruments. Following a 2023 rebrand, it boasts a contemporary design and provides advanced trading tools along with ultra-fast execution speeds, averaging 20ms.
Instruments Regulator Platforms CFDs, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, Futures, Crypto FMA, FSA BlackBull Invest, BlackBull CopyTrader, MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView, AutoChartist Min. Deposit Min. Trade Leverage $0 0.01 Lots 1:500 -
eToro is a leading multi-asset platform providing trading services across numerous CFDs, stocks, and cryptocurrencies. Since its 2007 inception, it has attracted millions of traders worldwide. It operates with authorisation from top regulators such as the FCA and CySEC. Its social trading feature is especially well-regarded. Crypto investments are high-risk and possibly unsuitable for retail investors. There's a potential to lose all invested capital. Familiarise yourself with the risks. 61% of retail CFD accounts incur losses.
Instruments Regulator Platforms CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, ETFs, Smart Portfolios, Commodities, Futures, Crypto, NFTs FCA, ASIC, CySEC, FSA, FSRA, MFSA, CNMV, AMF eToro Web, CopyTrader, TradingCentral Min. Deposit Min. Trade Leverage $50 $10 1:30
Safety Comparison
Compare how safe the Corn are and what features they offer to protect traders.
| Broker | Trust Rating | FCA Regulated | Negative Balance Protection | Guaranteed Stop Loss | Segregated Accounts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepperstone | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | |
| XTB | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| IC Markets | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | |
| IC Trading | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ | |
| Fusion Markets | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | |
| BlackBull Markets | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | |
| eToro | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ |
Payments Comparison
Compare which popular payment methods the Corn support and whether they have trading accounts denominated in British Pounds (GBP).
| Broker | GBP Account | Debit Card | Credit Card | Neteller | Skrill | Apple Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepperstone | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| XTB | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
| IC Markets | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
| IC Trading | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ |
| Fusion Markets | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
| BlackBull Markets | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
| eToro | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
Mobile Trading Comparison
How good are the Corn at mobile trading using apps or other mobile interfaces.
| Broker | Mobile Apps | iOS Rating | Android Rating | Smart Watch App |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepperstone | iOS & Android | ✘ | ||
| XTB | iOS & Android | ✔ | ||
| IC Markets | iOS & Android | ✘ | ||
| IC Trading | iOS & Android | ✘ | ||
| Fusion Markets | iOS & Android | ✘ | ||
| BlackBull Markets | iOS & Android | ✘ | ||
| eToro | iOS & Android | ✘ |
Beginners Comparison
Are the Corn good for beginner traders, that might want an affordable setup to get started, along with good support and educational resources?
| Broker | Demo Account | Minimum Deposit | Minimum Trade | Support Rating | Education Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepperstone | ✔ | $0 | 0.01 Lots | ||
| XTB | ✔ | $0 | 0.01 Lots | ||
| IC Markets | ✔ | $200 | 0.01 Lots | ||
| IC Trading | ✔ | $200 | 0.01 Lots | ||
| Fusion Markets | ✔ | $0 | 0.01 Lots | ||
| BlackBull Markets | ✔ | $0 | 0.01 Lots | ||
| eToro | ✔ | $50 | $10 |
Advanced Trading Comparison
Do the Corn offer features that allow for more advanced trading strategies?
| Broker | Automated Trading | Pro Account | Leverage | VPS | AI | Low Latency | Extended Hours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepperstone | Expert Advisors (EAs) on MetaTrader | ✔ | 1:30 (Retail), 1:500 (Pro) | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ |
| XTB | - | ✔ | 1:30 | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ |
| IC Markets | Expert Advisors (EAs) on MetaTrader, cBots on cTrader, Myfxbook AutoTrade | ✘ | 1:30 (ASIC & CySEC), 1:500 (FSA), 1:1000 (Global) | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ |
| IC Trading | Expert Advisors (EAs) on MetaTrader, cBots on cTrader | ✘ | 1:500 | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ |
| Fusion Markets | Expert Advisors (EAs) on MetaTrader, cBots on cTrader | ✘ | 1:500 | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ |
| BlackBull Markets | Expert Advisors (EAs) on MetaTrader, cTrader Automate | ✘ | 1:500 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
| eToro | Automate your trades via CopyTrader - follow profitable traders. Open and close trades automatically when they do. | ✘ | 1:30 | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ |
Detailed Rating Comparison
Use this heatmap to compare our detailed ratings for all of the Corn.
| Broker | Trust | Platforms | Mobile | Assets | Fees | Accounts | Support | Research | Education |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepperstone | |||||||||
| XTB | |||||||||
| IC Markets | |||||||||
| IC Trading | |||||||||
| Fusion Markets | |||||||||
| BlackBull Markets | |||||||||
| eToro |
Our Take On Pepperstone
"Pepperstone is a premier trading platform, providing tight spreads, swift execution, and sophisticated charting tools for seasoned traders. Beginners benefit from no minimum deposit, comprehensive learning materials, and outstanding 24/7 support."
Pros
- Support for top-tier charting platforms such as MT4, MT5, TradingView, and cTrader. These tools accommodate different short-term trading methods, including algorithmic trading.
- The award-winning customer support can be accessed through phone, email, or live chat. During tests, response times have consistently been under 5 minutes.
- In recent years, Pepperstone has significantly enhanced the deposit and withdrawal process. By 2025, clients can use Apple Pay and Google Pay, while 2024 saw the introduction of PIX and SPEI for customers in Brazil and Mexico.
Cons
- Pepperstone's demo accounts expire after 30 days, which may not provide sufficient time to explore various platforms and evaluate trading strategies.
- Pepperstone doesn't offer cTrader Copy, a favoured feature for copying trades found in the cTrader platform, which is available on other platforms such as IC Markets. However, Pepperstone has launched its own user-friendly copy trading app.
- Although its market range has improved, its crypto offerings remain limited compared to brokers specialising in this sector, lacking real coin investment options.
Our Take On XTB
"XTB excels for novice traders with its superb xStation platform, minimal trading costs, no required deposit, and outstanding educational resources, many of which are fully integrated into the platform."
Pros
- Setting up an XTB account is straightforward and fully online, requiring only a few minutes. This simplicity eases new traders into the world of trading.
- XTB offers a diverse array of instruments, including CFDs on shares, indices, ETFs, commodities, forex, crypto, real shares, real ETFs, and share dealing, along with newly introduced Investment Plans. This allows XTB to serve both short-term traders and long-term investors efficiently.
- XTB processes withdrawals swiftly, paying within 3 business days, subject to the method and amount.
Cons
- The research tools at XTB are commendable but have the potential to excel further. Enhancing them with access to top-tier third-party services like Autochartist, Trading Central, and TipRanks would significantly elevate their offering.
- The demo account lasts only four weeks, posing a challenge for traders wanting to fully explore the xStation platform and refine short-term strategies before investing actual money.
- It is frustrating that XTB products do not allow traders to modify the default leverage level. Manually adjusting leverage can greatly reduce risk in forex and CFD trading.
Our Take On IC Markets
"IC Markets provides excellent pricing, swift execution, and easy deposits. With cutting-edge charting tools like TradingView and the Raw Trader Plus account, it continues to be a preferred option for intermediate and advanced traders."
Pros
- In 2025, IC Markets earned DayTrading.com's accolade for 'Best MT4/MT5 Broker' due to its top-tier MetaTrader integration. This achievement highlights the broker's continuous refinement over the years to enhance the platform experience.
- As a well-regulated and reputable broker, IC Markets focuses on client safety and transparency to provide a dependable global trading experience.
- IC Markets provides some of the industry's narrowest spreads, offering 0.0-pip spreads on major currency pairs. This makes it an extremely cost-effective choice for traders.
Cons
- The tutorials, webinars, and educational resources require enhancement, lagging behind competitors such as CMC Markets, which diminishes their appeal to novice traders.
- IC Markets provides metals and cryptocurrencies for trading through CFDs, though the selection is narrower compared to brokers such as eToro. This limits opportunities for traders focused on these asset classes.
- Interest is not paid on idle cash, a feature gaining popularity with alternatives such as Interactive Brokers.
Our Take On IC Trading
"IC Trading offers an ideal environment, featuring top-tier execution speeds of around 40 milliseconds, extensive liquidity, and advanced charting tools, perfect for scalpers, traders, and algorithmic traders."
Pros
- IC Trading provides exceptional flexibility, allowing traders to open as many as 10 live accounts and 20 demo accounts. This enables the management of distinct profiles for various activities, including manual and algorithmic trading.
- IC Trading offers top-tier spreads, with some major currency pairs like EUR/USD featuring spreads as low as 0.0 pips, making it an excellent choice for traders.
- The streamlined digital account setup allows traders to commence trading swiftly, eliminating lengthy paperwork. Testing shows the process takes mere minutes.
Cons
- The educational materials require significant enhancement unless accessed via the IC Markets website. This limitation is particularly disadvantageous for beginners seeking a thorough learning experience, especially when compared to industry leaders such as eToro.
- Customer support was inadequate during testing, with multiple live chat attempts going unanswered and emails ignored. This raises significant concerns regarding their capacity to manage urgent trading issues.
- Although IC Trading operates under the reputable IC Markets group, it is licensed by the FSC in Mauritius, a regulator known for its limited financial transparency and lack of robust safeguards.
Our Take On Fusion Markets
"Fusion Markets offers forex traders competitive pricing with minimal spreads, low commissions, and new TradingView integration. It is an excellent choice, especially for Australian traders, given its base and regulation by ASIC."
Pros
- With an average execution speed of approximately 37 milliseconds, traders can secure optimal prices more effectively, outpacing many competitors in rapidly changing markets.
- The selection of charting platforms and social trading features is outstanding. Options like MT4, MT5, cTrader, and the newer TradingView meet diverse trader preferences.
- The market analysis tools, Market Buzz and Analyst Views, are excellent for identifying opportunities and are seamlessly incorporated into the client dashboard.
Cons
- Traders from outside Australia need to register with loosely regulated international firms that offer limited protection, lacking both safeguards and negative balance protection.
- The demo account, lasting only 30 days, is limited in its effectiveness as a trading tool when used with a live account.
- The broker stands out with its extensive selection of currency pairs, surpassing most competitors. However, its alternative investment options are merely average, lacking stock CFDs outside the US.
Our Take On BlackBull Markets
"Following the upgrade to Equinix servers in New York, London, and Tokyo, BlackBull has reduced latency, making it a clear choice for stock CFD trading using ECN pricing."
Pros
- BlackBull provides everything a trader needs: execution speeds under 100ms, leverage as high as 1:500, and competitive spreads starting at 0.0 pips.
- BlackBull better suits budding traders after revamping its ECN Prime account. It now offers improved spreads, averaging 0.16 on EUR/USD, and eliminates the previous $2,000 minimum deposit requirement.
- After collaborating with ZuluTrade and Myfxbook, upgrading its CopyTrader, and activating cTrader Copy, BlackBull provides an exceptionally thorough trading experience.
Cons
- Despite enhancements such as webinars and tutorials in the Education Hub, our review indicates that the courses still require greater emphasis on elucidating broader economic factors affecting prices.
- Despite an expanding range of over 26,000 assets, including new additions to Asia Pacific indices, their offerings are primarily equities. The selection of currency pairs and indices remains average.
- Unlike many leading brokers, BlackBull imposes a bothersome $5 fee for withdrawals. This charge can reduce the overall cost-effectiveness, particularly for traders who regularly transfer funds.
Our Take On eToro
"eToro's social trading platform excels with its outstanding user experience and lively community chat, aiding beginners in spotting opportunities. It offers competitive fees on numerous CFDs and real stocks, alongside exceptional rewards for seasoned strategists."
Pros
- The web platform and mobile app receive higher user reviews and app rankings compared to leading competitors like AvaTrade.
- The broker offers excellent services for beginners, featuring commission-free stock trading, a low minimum deposit, and an unlimited demo account.
- There is an extensive online training academy offering a range of accessible resources, from concise articles to detailed courses.
Cons
- The minimum withdrawal is set at $30, accompanied by a $5 fee. This may impact traders with limited funds, particularly those just starting out.
- The only significant contact option, besides the in-platform live chat, is limited.
- The absence of extra charting platforms such as MT4 may deter experienced traders who rely on external software.
How Does Corn Trading Work?
Corn trading refers to the buying and selling of corn in the commodities marketplace. Buyers and sellers typically trade corn futures, which are agreements to buy or sell a specific amount of corn at a predetermined price and date in the future. These contracts allow investors to speculate on the future price of corn, and can be bought and sold on commodity exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX).
Alternatively, the top corn brokers offer derivatives like CFDs that allow retail traders to go long or short on the price of corn without taking delivery of bushels of the grain.
Corn is one of the most widely produced and traded agricultural commodities in the world, and is used in many industries like food and beverage production, animal feed, and biofuel.
The price of corn can be influenced by various factors, like weather conditions, supply and demand, geopolitical events, and government policies.
History
Corn has been an important crop for thousands of years, with commodity use dating back to ancient times. However, the modern corn trading industry emerged in the 19th century, with the development of commodity exchanges and futures markets.
The Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) was founded in 1848 and quickly became the primary marketplace for corn trading. Initially, corn traders at the CBOT would buy and sell physical corn directly with farmers and grain elevators, but in the late 19th century, futures contracts were introduced as a way to manage risk and stabilise prices over upcoming months and years.
By the early 20th century, corn futures became integral to the global commodities market, and were traded on exchanges around the world. The introduction of new technologies, such as telegraphs and later computers, helped to facilitate faster and more efficient corn trading.
Today, corn remains a widely traded agricultural commodity, with futures traded on exchanges such as the CME Group and the Intercontinental Exchange
Corn Price Chart
Note, the corn trading symbol may change at different brokers and platforms.
What Influences The Price of Corn?
- Weather conditions: Corn supply is sensitive to weather conditions, temperature, precipitation, and other weather patterns, which can impact crop yields and supply. In 2019, the UK’s Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA) reported that the country’s corn production had decreased due to a dry spring and summer. This led to a rise in corn prices, which affected UK farmers and traders who rely on the domestic corn market.
- Supply & demand: Corn is used in several industries, and changes in demand impact the price of corn. In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic caused disruptions in the global supply chain, creating a shortage of corn-based products in the UK, amongst other countries. A decrease in corn production and logistical issues in transporting corn to the UK resulted in corn prices rising.
- Ethanol production: Ethanol is a biofuel that is made from corn in many countries, including the United States. Changes in the demand for ethanol can have a direct impact on the price of corn at online brokers.
- Government policies: Governments around the world often implement policies that impact the price of corn, such as subsidies, tariffs, and import/export regulations.
- Currency exchange rates: Corn is a globally traded commodity, and changes in exchange rates between currencies can impact the price of corn in different countries, including at UK brokers.
- Competition from other crops: Corn competes with other crops, such as soybeans for acreage and resources. Changes in the price of these competing crops can impact the price of corn.
- Current events: Major events can impact corn trading prices at brokers. For example, in 2017, Brexit had an impact on corn; the value of the British pound dropped significantly, making imports of corn more expensive for UK buyers. This led to higher prices for corn-based products, affecting UK consumers and businesses.
How To Trade Corn
Investors can speculate on corn prices through several vehicles:
- Shares of Agricultural Companies: Traders can invest in the shares of companies involved in the production, processing, or distribution of corn, such as agricultural machinery manufacturers or food and beverage companies that use corn as a primary ingredient. Publicly-traded companies operating in the corn industry include Archer-Daniels-Midland Company (ADM) and Ingredion Incorporated (INGR).
- Contracts for Difference: Popular with retail investors, CFDs allow traders to speculate on rising and falling prices of corn without taking ownership of bushels of the grain. Leverage also enables traders to increase their purchasing power with a small cash deposit.
- Futures: Futures or mini futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell a specific amount of corn at an agreed price and date in the future. Corn futures are traded on major exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE).
- Options: Options contracts give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell corn at a certain price at a future date. Options contracts can be used to manage risk and speculate on the future price of corn.
- Exchange-Traded Funds: ETFs that track the price of the corn sector or corn-related companies can be traded on major stock exchanges, such as the NYSE or NASDAQ.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC): OTC markets are decentralised trading venues allowing buyers and sellers to trade directly with each other, without going through a centralised exchange. OTC trading of corn and other commodities is typically conducted through online brokers and dealers.
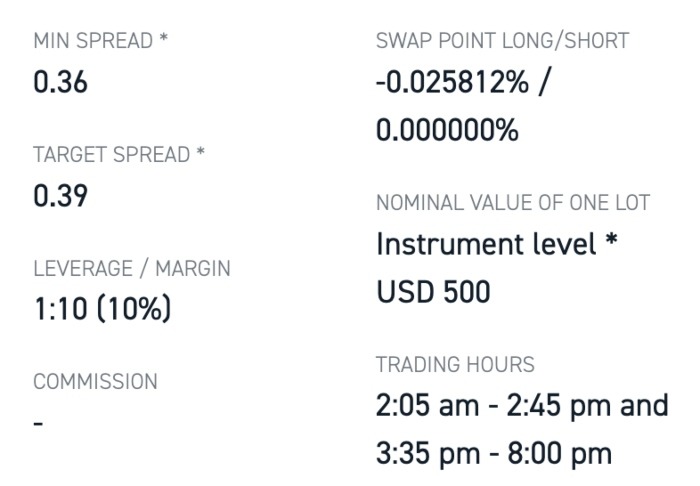
XTB Corn Trading Conditions
Why Trade Corn?
- High Liquidity: Corn is one of the most heavily traded commodities, and therefore there is high liquidity in corn futures and options markets, making it easy for traders to buy and sell contracts at competitive prices.
- Price Transparency: The price of corn is widely reported and tracked, allowing traders to access real-time market data and make informed trading decisions.
- Diversification: Corn is globally traded and can be used to diversify portfolios. By investing in corn futures or related exchange-traded funds (ETFs), for example, traders can spread their risk across a variety of asset classes and trading vehicles.
- Risk Management: Corn futures can be used as a hedging tool. For example, a farmer may use futures contracts to lock in a guaranteed price for their crop before it is even harvested, providing protection against price fluctuations. Equally, traders can use corn as a hedge against other markets.
- Transparency: Trading corn contracts is often conducted on regulated exchanges, which provides transparency and standardised contract terms.
Risks Of Trading Corn
- Price Volatility: The price of corn can be volatile, influenced by a range of factors such as weather, supply and demand, and geopolitical events. This can create uncertainty and risk resulting in losses if traders make incorrect forecasts.
- Weather Risk: Corn is highly dependent on weather conditions, which have an impact on crop yields and supply. This makes the market unpredictable and harder for traders to predict future price movements.
- Margin Requirements: Derivative contracts require traders to maintain margin at their corn brokers to cover potential losses. This can be a significant financial commitment.
- Market Manipulation: The corn market is susceptible to manipulation by traders or other market participants. This can create artificially high or low prices and risk for beginner traders.
- Regulatory Risk: Changes in government policies or regulations can impact prices and corn trading activity at leading brokers and platforms.
Strategies
- Seasonal Trading: Analysing historical price data can help identify seasonal trends in the corn market. For example, if the price of corn tends to rise in the spring when planting season begins, a trader may look to buy corn futures contracts in the winter in anticipation of this price increase.
- Spread Trading: Spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling related contracts to profit from price differentials. For example, a trader may buy a corn futures contract for delivery in December and simultaneously sell a corn futures contract for delivery in March, with the expectation that the price difference between the two contracts will narrow.
- Technical Analysis: Analysing historical price data and identifying patterns or trends in the corn market can inform trading decisions. Traders using technical analysis may use historical charts, trendlines, and technical indicators to identify potential entry and exit points. TradingView is a popular charting tool for corn trading.
- Fundamental Analysis: Analysing supply and demand factors help inform corn trading forecasts. This includes assessing weather forecasts, government reports on crop yields, and global demand for corn-based products.
- News Trading: News trading involves monitoring events and updates that influence the corn market, like weather forecasts, crop reports, or political developments. Traders using this strategy may enter or exit trades based on or in anticipation of the latest crop trading news.
Note, corn brokers may have restrictions on the strategies that can be used on their trading platforms.
Corn Trading Times
Trading times are traditionally based on the schedule of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), which is where corn futures are primarily traded. The CME operates on Central Time with corn futures trading hours:
- Monday – Friday: 8:30 AM – 1:20 PM CT
- Sunday: 7:00 PM – 7:45 AM CT, then 8:30 AM – 1:20 PM CT
Note that these trading times apply to corn futures contracts. Other forms of corn trading, such as CFDs or corn-related stocks, may have different trading hours.
Some corn brokers also offer extended trading hours or pre-market trading. Trading hours may be subject to change due to market holidays or other events.
Bottom Line On Corn Trading
Corn trading can be lucrative for traders looking to invest in agricultural commodities. Understanding the factors that influence corn prices, such as weather patterns, supply and demand, and government policies, is key to successful corn trading. Investors can trade corn through multiple vehicles, including CFDs, ETFs, futures and options.
Head to our ranking of the best corn brokers to start trading.
FAQ
What Is Corn Trading?
Corn trading involves buying and selling the grain either via spot or derivatives like futures, options and CFDs. Traders can also speculate in the shares of publicly-traded companies that operate in the production, distribution and marketing of corn.
What Factors Influence The Price Of Corn?
Corn prices are influenced by a range of factors, including weather patterns, supply and demand, government policies, global trade dynamics, and more. Key drivers are Chinese demand and production in major countries like Brazil. Understanding these factors is key to building a successful corn trading strategy.
What Are The Risks Of Trading Corn?
Like any online trading opportunity, investing in corn involves risks. This includes market volatility due to unforeseen weather events and geopolitical events that cause supply chain issues, such as the Russia-Ukraine war. Corn exports from Ukraine were down approximately 20% in 2022, pushing up prices. Corn trading limits and halts may also impact strategies.
What Are Popular Corn Trading Strategies?
Popular corn trading strategies include seasonal trading, trend-following approaches, technical analysis, and spread trading. However, investors should develop a corn trading plan that aligns with their risk tolerance, investing style, and market outlook.
How Do I Choose A Corn Trading Broker?
When comparing corn brokers, consider the availability of futures, options and CFDs, spreads and fees, execution speeds, access to commodity data, and a license from the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). Alternatively, choose from our list of the best corn trading brokers.

